1000 Types of Succulents With Pictures and Names
Succulents are the cool, fleshy plants that can survive in super dry places like deserts. With thick leaves to store water, they’ve adapted amazing ways to go months without rain.
There are over 10,000 different succulents and nurseries make new weird hybrids all the time. Get ready to see their funky shapes, bright colors and learn how they thrive when everything else dries up.
This guide shows pics and names of 1000 succulents – a window into one of nature’s toughest plant families.

This page contains affiliate links, and as an affiliate, we earn from qualifying purchases which means we receive a small commission when you make a purchase, at zero cost to you.
Contents
- 1 Types of Succulents With Pictures and Names
- 1.1 Adenium
- 1.2 Adromischus
- 1.3 Aeonium
- 1.4 Agave
- 1.5 Albuca
- 1.6 Aloe
- 1.7 Aloinopsis
- 1.8 x Alworthia
- 1.9 Anacampseros
- 1.10 Antegibbaeum
- 1.11 Antimima
- 1.12 Aptenia
- 1.13 Argyroderma
- 1.14 Astridia
- 1.15 Astroloba
- 1.16 x Astroworthia
- 1.17 Avonia
- 1.18 Bergeranthus
- 1.19 Bijlia
- 1.20 Braunsia
- 1.21 Callisia
- 1.22 Carruanthus
- 1.23 Cephalophyllum
- 1.24 Ceropegia
- 1.25 Cheiridopsis
- 1.26 Conophytum
- 1.27 Corpuscularia
- 1.28 Cotyledon
- 1.29 Crassula
- 1.30 x Cremnosedum
- 1.31 Dinteranthus
- 1.32 Dischidia
- 1.33 Dudleya
- 1.34 Dyckia
- 1.35 Ebracteola
- 1.36 Echeveria
- 1.37 Echidnopsis
- 1.38 Euphorbia
- 1.39 Faucaria
- 1.40 Fenestaria
- 1.41 Frithia
- 1.42 Furcraea
- 1.43 x Gasteraloe
- 1.44 x Gasterhaworthia
- 1.45 Gasteria
- 1.46 Gibbaeum
- 1.47 Glottiphyllum
- 1.48 Graptopetalum
- 1.49 x Graptosedum
- 1.50 x Graptoveria
- 1.51 Haworthia
- 1.52 Hesperaloe
- 1.53 Huernia
- 1.54 Ihlenfeldtia
- 1.55 Jensenobotrya
- 1.56 Juttadinteria
- 1.57 Kalanchoe
- 1.58 Lampranthus
- 1.59 Lapidaria
- 1.60 Larryleachia
- 1.61 Lenophyllum
- 1.62 Lithops
- 1.63 x Mangave
- 1.64 Monanthes
- 1.65 Monilaria
- 1.66 Neohenricia
- 1.67 Odontophorus
- 1.68 Orbea
- 1.69 Orostachys
- 1.70 Oscularia
- 1.71 Othonna
- 1.72 Pachyphytum
- 1.73 x Pachyveria
- 1.74 Peperomia
- 1.75 Pleiospilos
- 1.76 Portulaca
- 1.77 Portulacaria
- 1.78 Prenia
- 1.79 Pseudolithos
- 1.80 Rabiea
- 1.81 Rhombophyllum
- 1.82 Rosularia
- 1.83 Sansevieria
- 1.84 x Sedeveria
- 1.85 Sedum
- 1.86 Sempervivum
- 1.87 Senecio
- 1.88 Sinocrassula
- 1.89 Stapelia
- 1.90 Stapelianthus
- 1.91 Stapeliopsis
- 1.92 Tavaresia
- 1.93 Titanopsis
- 1.94 Trachyandra
- 1.95 Tradescantia
- 1.96 Trichodiadema
- 1.97 Tromotriche
- 1.98 Tylecodon
- 1.99 Umbilicus
- 1.100 Xerosicyos
- 1.101 Yucca
- 2 How do I Identify a Succulent?
Types of Succulents With Pictures and Names
Adenium
Adenium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1819. It is native to Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. Adeniums are appreciated for their colorful flowers, but also for their unusual, thick caudices. They can be grown for many years in a pot and are commonly used for bonsai.
Examples of Adenium succulents:




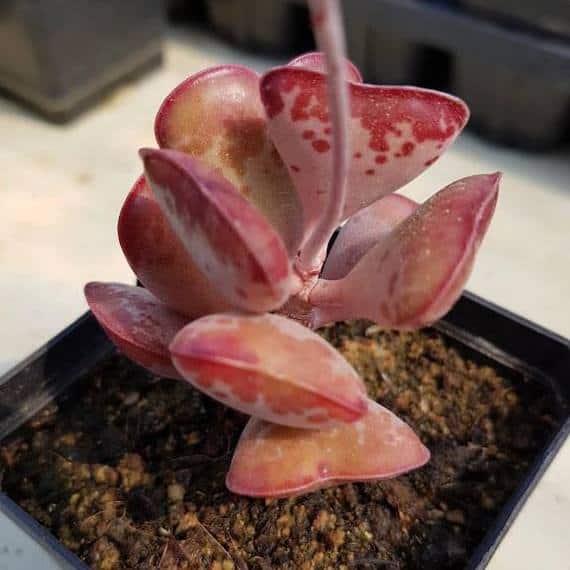
Adromischus
Adromischus is a genus of easily propagated leaf succulents from the Crassulaceae family. Adromischus are endemic to southern Africa. The name comes from the ancient Greek “adros” (meaning thick) and “mischos” (meaning stem).
Examples of Adromischus succulents:




Related Post:
30 Exquisite Adromischus Species [With Pictures]
Aeonium
Aeonium, the tree houseleeks, is a genus of about 35 species of succulent, subtropical plants of the family Crassulaceae. Many species are popular in horticulture. The genus name comes from the ancient Greek “aionos” (ageless). While most of them are native to the Canary Islands, some are found in Madeira, Morocco, and in East Africa (for example in the Semien Mountains of Ethiopia).
Examples of Aeonium succulents:




Related Posts:
58 Stunning Aeonium Varieties [With Pictures]
Agave
Agave is a genus of monocots native to the hot and arid regions of the Americas, although some Agave species are also native to tropical areas of South America. The genus Agave is primarily known for its succulent and xerophytic species that typically form large rosettes of strong, fleshy leaves.
Examples of Agave succulents:




Related Posts:
70+ Types of Agave [With Pictures]
Albuca
Albuca is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae. The genus is distributed mainly in southern and eastern Africa, with some species occurring in northern Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. Plants of the genus are known commonly as slime lilies. These are perennial herbs growing from bulbs.
Examples of Albuca succulents:




Aloe
Aloe is a genus containing over 500 species of flowering succulent plants. The genus is native to tropical and southern Africa, Madagascar, Jordan, the Arabian Peninsula, and various islands in the Indian Ocean (Mauritius, Réunion, Comoros, etc.). A few species have also become naturalized in other regions (Mediterranean, India, Australia, North and South America, Hawaiian Islands, etc.).
Examples of Aloe succulents:




Related Post:
40+ Interesting Types Of Aloe Plants [With Pictures]
Aloinopsis
Aloinopsis is a genus of ice plants from South Africa. Aloinopsis species have a rather large tuberous root system and are occasionally cultivated for their looks. They also tend to grow more “heads” when they are raised. Most Aloinopsis are winter growers and can react badly to too much water at the wrong time.
Examples of Aloinopsis succulents:




x Alworthia
x Alworthia are succulent plants that are hybrid crosses between Aloe and Haworthia.
Examples of x Alworthia succulents:


Anacampseros
Anacampseros is a genus comprising about a hundred species of small perennial succulent plants native to Southern Africa. Plants in the genus Anacampseros are perennial. In habit they are small undershrubs or sprawling herbs that may form dense mats. Mature plants of many of the species form a small caudex or a tuberous root-stock.
Examples of Anacampseros succulents:




Related Post:
25 Types of Anacampseros [With Pictures]
Antegibbaeum
The genus Antegibbaeum is a flowering succulent plant in the family Aizoaceae. There is only one species in the monospeciefic genus Antegibbaeum.
Example of Antegibbaeum succulent:

Antimima
Antimima is a succulent plant genus in the family Aizoaceae, indigenous to South Africa and Namibia. The Greek word “antimimos” means “imitating”, and refers to the similarity some species have to the different genus Argyroderma. The species of this varied genus typically grow as dense cushions or mats. Otherwise, Antimima species are very similar in their superficial looks to the related genus Ruschia, with 3-sided waxy succulent leaves, and pink or white flowers.
Examples of Antimima succulents:




Aptenia
Aptenia is a small genus of flowering plants in the family Aizoaceae. They are native to southern Africa. These are succulent subshrubs growing from a system of fibrous, often fleshy roots. There are only 4 species of Aptenia succulents.
Examples of Aptenia succulents:




Related Posts:
4 Types of Aptenia [With Pictures]
Argyroderma
Argyroderma is a genus of flowering succulent plants in the iceplant family Aizoaceae from South Africa.
Examples of Argyroderma succulents:




Astridia
Astridia is a genus of plants in the family Aizoaceae. It is named after the wife Astrid of the German botanist and archaeologist Gustav Schwantes (1881 – 1960).
Examples of Astridia succulents:




Astroloba
Astroloba is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asphodelaceae, subfamily Asphodeloideae, native to the Cape Province of South Africa.
Examples of Astroloba succulents:




x Astroworthia
x Astroworthia is a hybrid genus between Astroloba and Haworthia.
Example of x Astroworthia succulent:

Avonia
Avonia is a genus of succulent plants in the Portulacaceae family. It was formerly a subgenus of Anacampseros and became its own genus in 1994.
Examples of Avonia succulents:




Bergeranthus
The genus Bergeranthus is a member of the Aizoaceae family, in the major group Angiosperms (flowering plants). It is a small genus of 10 species that all occur in the Eastern Cape of South Africa. The genus Bergeranthus occurs only in the spring and autumn rainfall area of the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa.
Examples of Bergeranthus succulents:




Bijlia
Bijlia is a genus of flowering succulent plants in the ice plant family Aizoaceae from South Africa. The genus Bijlia is restricted to the Little Karoo in the Western Cape Province, South Africa.
Examples of Bijlia succulents:



Braunsia
Braunsia is a genus of flowering succulent plants in the ice plant family Aizoaceae from the southwestern part of the Western Cape Province in South Africa.
Examples of Braunsia succulents:




Callisia
Callisia is a genus of flowering plants in the spiderwort family, Commelinaceae. Members of the genus are commonly known as roselings. It is native to the Western Hemisphere from the southern United States to Argentina. The generic name is derived from the Greek word καλλον, meaning “beauty.”
Examples of Callisia succulents:




Carruanthus
Carruanthus is a genus of flowering plants from the ice plant family Aizoaceae.
Examples of Carruanthus succulents:


Cephalophyllum
Cephalophyllum is a genus of flowering plants from the ice plant family Aizoaceae.
Examples of Cephalophyllum succulents:




Related Post:
27 Types Of Cephalophyllum Succulents [With Pictures]
Ceropegia
Ceropegia is a genus of plants within the family Apocynaceae, native to Africa, southern Asia, and Australia. They have many common names including lantern flower, parasol flower, parachute flower, bushman’s pipe, string of hearts, snake creeper, wine-glass vine, rosary vine, and necklace vine.
Examples of Ceropegia succulents:




Cheiridopsis
Cheiridopsis is a genus that consists of 100 species of flowering succulent perennial plants, native to semi-arid regions in the far west of Namibia and South Africa.
Examples of Cheiridopsis succulents:




Related Post:
16 Unique Types of Cheiridopsis Succulents [With Pictures]
Conophytum
Conophytum is a genus of South African and Namibian succulent plants that belong to the family Aizoaceae. The name is derived from the Latin conus and Greek phytum. The plants are also known as knopies, waterblasies, sphaeroids, conos, cone plants, dumplings, or button plants.
Examples of Conophytum succulents:




Related Post:
143 Types of Conophytum [With Pictures]
Corpuscularia
Corpuscularia is a small genus of succulent plants in the ice plant family Aizoaceae, from the coastal belt of the southern Cape, South Africa.
Examples of Corpuscularia succulents:


Cotyledon
Cotyledon is a genus of succulent plants in the Crassulaceae family. Mostly from Southern Africa, they also occur throughout the drier parts of Africa as far north as the Arabian peninsula. Members of the genus are shrublets, generally succulent, with fleshily woody, brittle stems and persistent succulent leaves.
Examples of Cotyledon succulents:




Crassula
Crassula is a genus of succulent plants containing about 200 accepted species, including the popular jade plant (Crassula ovata). They are members of the stonecrop (Crassulaceae) family and are native to many parts of the globe, but cultivated succulent varieties originate almost exclusively from species from the Eastern Cape of South Africa.
Examples of Crassula Succulents:




Related Posts:
22 Popular Kinds of Jade Plants [With Pictures]
12 Crassula Lower Classifications [With Pictures]
x Cremnosedum
× Cremnosedum is a hybrid genus produced from crosses involving the genera Cremnophila and Sedum.
Example of x Cremnosedum succulent:

Dinteranthus
Dinteranthus is a genus of plants in the family Aizoaceae. It occurs in the arid northwestern parts of the Northern Cape Province, South Africa and the southeastern parts of Namibia.
Dinteranthus is an intriguing solitary or clumping plant with attractive bodies and flowers that are very similar to Lithops in shape and colors but with no apparent dormant period. Its sunken growth form is understood as a development parallel to that in Lithops.
Examples of Dinteranthus succulents:

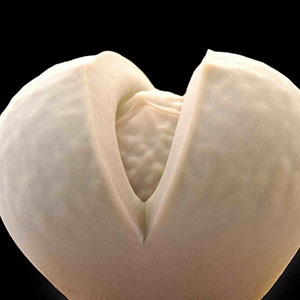

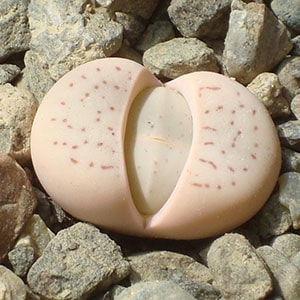
Dischidia
Dischidia is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae. They are epiphytes native to tropical areas of China, India and most areas of Indo-China.
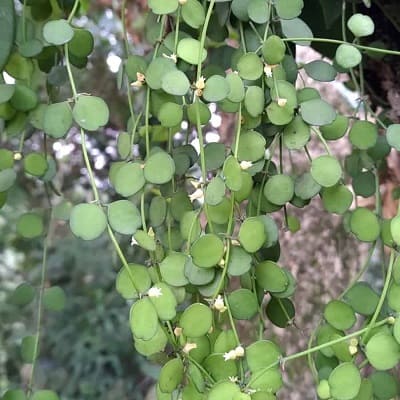
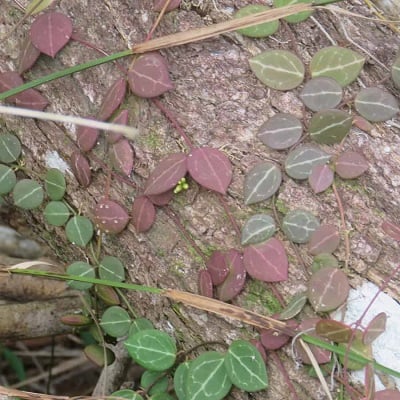
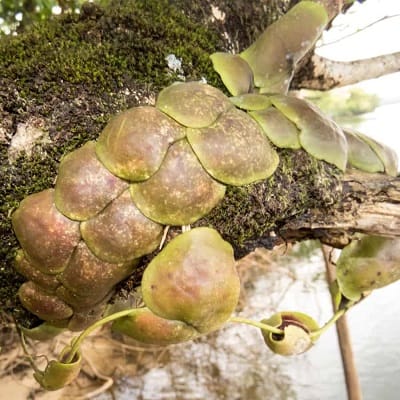
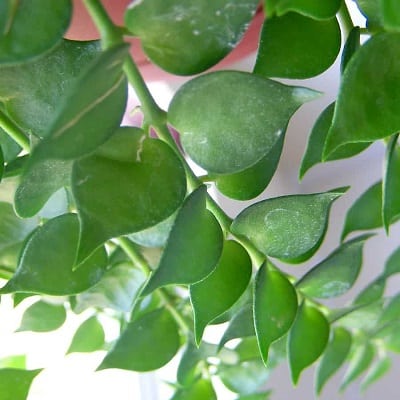




Related Posts:
16 Types of Dischidia [With Pictures]
Dudleya
Dudleya is a genus of succulent perennial plants, consisting of about 45 species in southwestern North America. Many plants in the Dudleya genus were formerly classified as Echeveria.
Dudleya species are widespread in their range, typically found in rock outcroppings, cliff faces, or road cuts, where their leaves help them store water in a setting too dry for most types of plants. Most are small and inconspicuous when not in bloom.
The genus is named after William Russell Dudley, the first head of the botany department at Stanford University.
In horticulture, Dudleya should be planted at an angle. This allows accumulated water to drain from the nestlike center of the plant, thus preventing microbial decay.
Examples of Dudleya succulents:




Related Posts:
52 Types of Dudleya [With Pictures]
Dyckia
Dyckia is a genus of plants in the family Bromeliaceae, subfamily Pitcairnioideae. Considered to be the most ancient lineage of bromeliads, they are endemic to arid and high-altitude regions of Brazil and the central part of South America.
Examples of Dyckia succulents:




Ebracteola
Ebracteola is a small genus of flowering succulent plants in the ice plant family Aizoaceae.
Examples of Ebracteola succulents:




Echeveria
Echeveria is a large genus of flowering plants in the family Crassulaceae, native to semi-desert areas of Central America, Mexico and northwestern South America.
Many Echeveria species are popular as ornamental garden plants. They are drought-resistant, although they do better with regular deep watering and fertilizing. Most will tolerate shade and some frost, although hybrids tend to be less tolerant.
Most lose their lower leaves in winter; as a result, after a few years, the plants lose their compact appearance and need to be re-rooted or propagated. In addition, if not removed, the shed leaves may decay, harboring fungus that can then infect the plant.
Examples of Echeveria succulents:




Related Post:
160+ Unique Echeveria Types [With Pictures]
Echidnopsis
Echidnopsis is a genus of succulent, cactus-like plants in the family Apocynaceae. They are native to eastern Africa and the Arabian Peninsula.
Examples of Echidnopsis succulents:




Euphorbia
Euphorbia is a very large and diverse genus of flowering plants, commonly called spurge, in the spurge family. There are over 2000 species of Euphorbias in the world. They range from annual weeds to trees. They all have latex and a unique flower structure. A significant percentage is succulent, but they are mostly originating from Africa and Madagascar.
The Euphorbias are named after a Greek surgeon called Euphorbus. He was a physician of Juba II who was the Romanised king of a North African kingdom and is supposed to have used their milky latex as an ingredient for his potions.
Examples of Euphorbia succulents:




Related Post:
200+ Types of Euphorbia Plants [With Pictures]
Faucaria
The popular genus Faucaria is found in the Eastern Cape Province into the Little and Great Karoo of the Western Cape Province. The genus is characterized by its triangular, mottled leaves, the margins of which have rows of soft teeth that curve inward. The flower color ranges from yellow to white and even pink.
The various species make excellent pot subjects and have been cultivated in Europe for over three hundred years. All species are active in summer. Some species, such as F. tigrina, are quite hardy, while others can be prone to stem rot. Plants are easily propagated by seed.
Examples of Faucaria succulents:




Fenestaria
Fenestraria is a monotypic genus comprising only one species and one subspecies. On each leaf of this plant, there is a transparent window-like area at the top, it is for these windows (in Latin “fenestra”) that the genus name is derived from.
Commonly called “Baby Toes”, Fenestaria has small club-shaped leaves with fenestrate ends and form large clumps by offsetting. Flower colors range from pure white to rich golden yellow. The var. aurantiaca succulent identifier are the flowers that are bright golden yellow (never white).
Examples of Fenestaria succulents:


Frithia
Frithia is a genus of succulent plant in the family Aizoaceae, indigenous to several small rocky areas in the vicinity of Gauteng Province, South Africa. They are low-growing evergreen succulent perennials with erect, club-shaped leaves with a clear window at the apex, and solitary, daisy-like red to purple flowers in late winter.
Examples of Frithia succulents:


Furcraea
Furcraea plants are originally from the tropical regions of both Americas but today, you can find them in many different parts of the world like Thailand, India, Portugal and Australia thanks to the love everyone seems to have for domestic gardening. Furcraea foetida (Green Aloe) is the most commonly grown domestic species and smells like rotten leaves.
Examples of Furcraea succulents:




Related Post:
18 Types of Furcraea False Agave [With Pictures]
x Gasteraloe
x Gasteraloe is a genus of hybrid plants, from mixtures of species from the Aloe or Aristaloe and Gasteria genera. x Gasteraloe hybrids are typically stemless or almost stemless. Their succulent leaves, which are usually spotted or marked and have toothed margins, form rosettes.
Examples of x Gasteraloe succulents:




x Gasterhaworthia
x Gasterhaworthia is a hybrid genus produced from crosses involving the genera Gasteria and Haworthia.
Examples of x Gasterhaworthia succulents:




Gasteria
Gasteria is a genus of succulent plants, native to South Africa. It sometimes goes by the colloquial name “ox tongue,” after the long, rough texture of the leaves. The plant is named for the sac-like shape of its flowers, which are supposed to resemble a stomach.
Examples of Gasteria succulents:




Related Posts:
9 Rare Types of Gasteria Succulents [With Pictures]
Gibbaeum
Gibbaeum is a genus of about 21 species of small succulent plants of the family Aizoaceae, indigenous to the Little Karoo region of South Africa. The name “Gibbaeum” comes from the Latin gibbosus (hunchback).
Examples of Gibbaeum succulents:
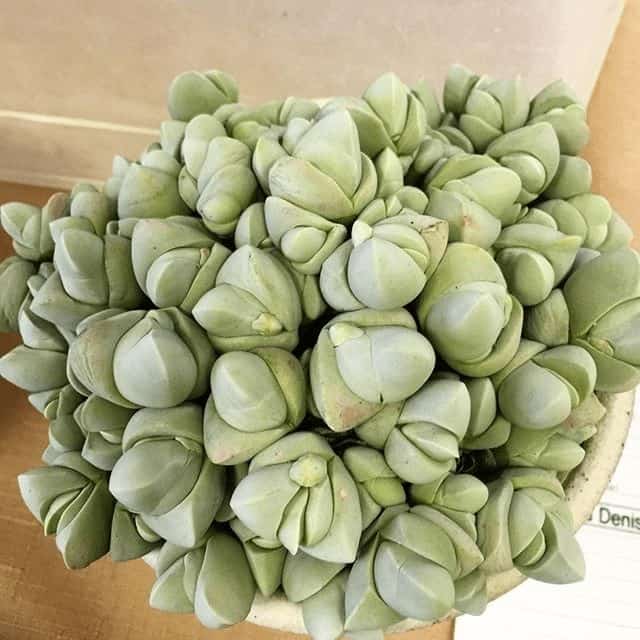




Glottiphyllum
Glottiphyllum is a genus of about 57 species of succulent subtropical plants of the family Aizoaceae. It is closely related to the Gibbaeum and Faucaria genera.
The plants of the genus Glottiphyllum are small and characterized by long fleshy leaves, oblong, sometimes wider or more cylindrical, depending on the species: it is the shape of the leaves that gives the name to this genre.
The stems are short, not particularly hard, and give the plant a drooping posture: the plant is well suited in fact to be grown in hanging baskets or pots, from which the long leaves fall down with a very pleasant decorative effect.
The flowers are yellow, shaped like a daisy and rather large; the bloom is in winter and the flowers tend to open only in the late afternoon. The length of the leaves, which gives the measure of the plant as a whole, since it is the most visible part, can reach 10-12 cm.
Examples of Glottiphyllum succulents:




Graptopetalum
Graptopetalum (leatherpetal) is a plant genus of the family Crassulaceae. They are perennial succulent plants and native to Mexico and Arizona. They grow usually in a rosette. There are around 19 species in this genus.
The name for the genus comes from the Greek words “graptos”, meaning “marked” or “inscribed” and “petalon”, meaning “petals” for the markings on the flower petals of many of the species.
Examples of Graptopetalum succulents:




Related Post:
20 Types Of Graptopetalum [With Pictures]
x Graptosedum
x Graptosedum are succulent plants that are hybrid crosses between Graptopetalum and Sedum.
Examples of x Graptosedum succulents:




Related Post:
5 Special Graptosedum Varieties [With Pictures]
x Graptoveria
x Graptoveria are succulent plants that are hybrid crosses between Graptopetalum and Echeveria.
Examples of x Graptoveria succulents:




Related Post:
20 Unique Graptoveria Types [With Pictures]
Haworthia
Haworthia is a large genus of small succulent plants endemic to Southern Africa (Mozambique, Namibia, Lesotho, Swaziland and South Africa). Like the aloes, they are members of the subfamily Asphodeloideae and they generally resemble miniature aloes, except in their flowers, which are distinctive in appearance. They are popular garden and container plants.
The leaves can be hard, soft, long, short, stacked, grass-like, and in a full range of colors with windows, lines, flecks, bumps, bands, pearls, hairs, spines, and rasps. Haworthia taxonomy, as indicated by the sheer number of sub-specific succulent varieties, is complicated and far from a settled matter.
Examples of Haworthia succulents:




Related posts:
14 Haworthia Types [With Pictures]
Hesperaloe
Hesperaloe, or false yucca, refers to a whole genus of flowering succulents that belong to the family Asparagaceae and subfamily Agavoideae. Hesperaloe gets its name from “hesperos”, which means “western” in Greek and its second half, “aloe”, because of its resemblance to the aloe plant.
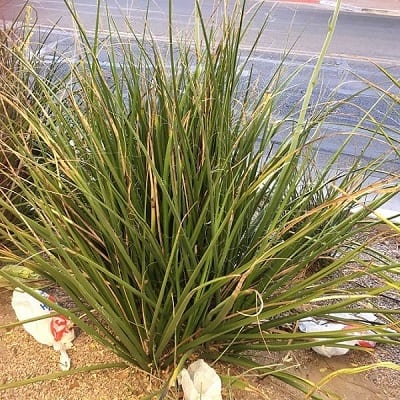
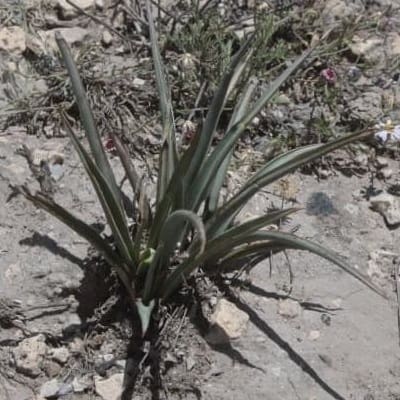
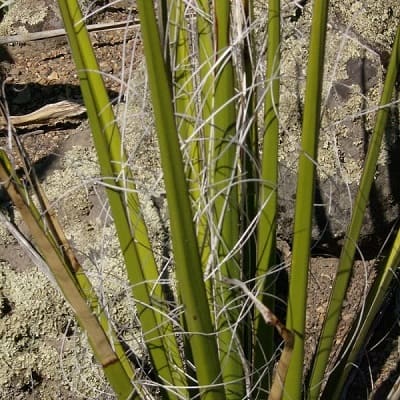
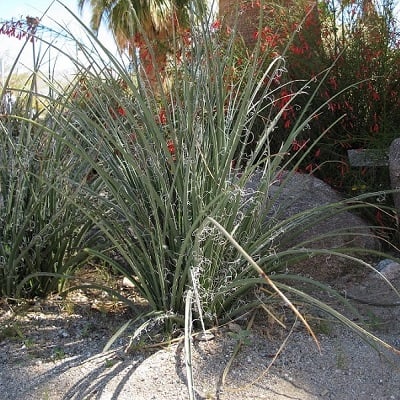




Related Posts:
7 Types of Hesperaloe [With Pictures]
Huernia
The genus Huernia consists of perennial, stem succulents from Eastern and Southern Africa and Arabia, first described as a genus in 1810. The flowers are five-lobed, usually somewhat more funnel- or bell-shaped than in the closely related genus Stapelia, and often striped vividly in contrasting colors or tones, some glossy, others matte and wrinkled depending on the species concerned. Frequently the flowers are colored a variation of red, yellow or brown.
The genus is considered close to the genera Stapelia and Hoodia. Phylogenetic studies have shown the genus to be monophyletic, and most closely related to the genus Tavaresia, and to a widespread branch of stapeliads comprising the genera Orbea, Piaranthus and Stapelia.
Examples of Huernia succulents:




Related Post:
46 Types of Huernia [With Pictures]
Ihlenfeldtia
Ihlenfeldtia is a succulent genus from the ice plant family of Aizoaceae. Both species of Ihlenfeldtia occur in the Northern Cape Province, South Africa. The compact plants have keeled three-sided leaves and showy flowers. They resemble Cheiridopsis species but the seed capsules resemble those of Titanopsis.
They blossom in early spring and the flowers open midday and close at dusk. They need warmth, well-drained soil for succulents, and plenty of water during their active season in autumn and winter. They are easily propagated by seed.
Examples of Ihlenfeldtia succulents:


Jensenobotrya
Jensenobotrya is a genus of succulent plant in the family Aizoaceae that is endemic to Namibia. Its natural habitat is rocky areas. It grows at Dolphin Head in Spencer Bay where it obtains moisture from the saline mists. It is threatened by habitat loss. Jensenobotrya lossowiana is the only species of genus Jensenobotrya.
Example of Jensenobotrya succulent:

Juttadinteria
Juttadinteria genus is an Aizoaceae from Namibia’s desert areas and savannahs. They are small plants: they reach 20-25 cm in height, they have slow growth. From the green stem, a series of triangular, succulent (as well as the stem, the rest) and elongated leaves come out.
They grow paired, placing themselves on opposite sides of the stem. The flowers are daisy-shaped, mostly white, and flourish in autumn and winter: due to the origin of the plant, below the equator, its life cycle is in fact inverted.
Examples of Juttadinteria succulents:




Kalanchoe
Kalanchoe is a genus of about 125 species of tropical, succulent flowering plants in the family Crassulaceae, mainly native to Madagascar and tropical Africa. Most are shrubs or perennial herbaceous plants, but a few are annual or biennial. The largest, Kalanchoe beharensis from Madagascar, can reach 6 m (20 ft) tall, but most species are less than 1 m (3 ft) tall.
Kalanchoes are characterized by opening their flowers by growing new cells on the inner surface of the petals to force them outwards, and on the outside of the petals to close them. Kalanchoe flowers are divided into 4 sections with 8 stamens. The petals are fused into a tube, in a similar way to some related genera such as Cotyledon.
Examples of Kalanchoe succulents:




Related Posts:
6 Peculiar Mother of Thousands Varieties [With Pictures]
40+ Kalanchoe Lower Classifications [With Pictures]
Lampranthus
Lampranthus is a fairly large genus with 100 to 150 species coming from South Africa. It provides some of the most spectacular displays of bright flowers from the succulent world and is widely used as ground cover, either annual or perennial as the climate allows. Several species are used for landscaping and vary from shrubby to trailing. All the species tend to become woody as they age.
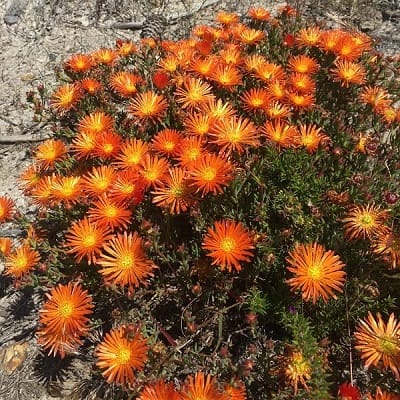
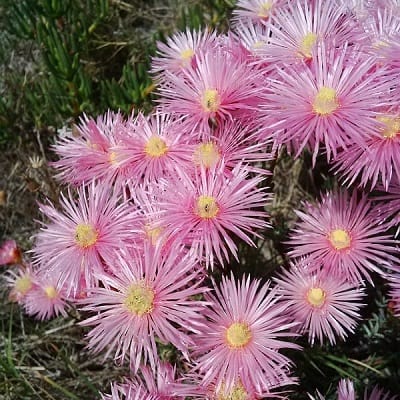
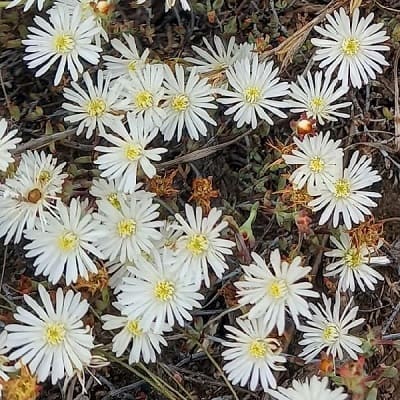
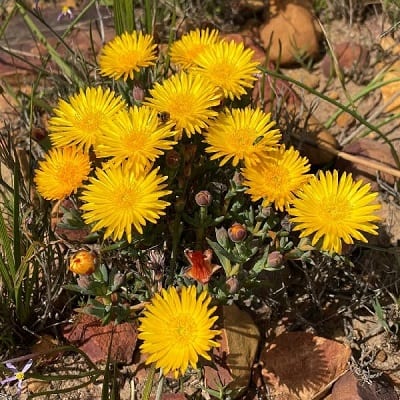




Related Post:
67 Types of Lampranthus [With Pictures]
Lapidaria
Lapidaria is a monotypic genus of dwarf succulent plants in the family Aizoaceae. The only species it contains is Lapidaria margaretae, also known as the Karoo rose.
Example of Lapidaria succulent:

Larryleachia
Larryleachia is a genus of stapeliad succulent flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae. Phylogenetic studies have shown the genus to be monophyletic, and most closely related to the stapeliad genera Richtersveldtia and Notechidnopsis. Marginally more distantly related is a sister branch of related genera including Lavrania and Hoodia.
Examples of Larryleachia succulents:




Lenophyllum
Lenophyllum is a genus of flowering plants in the orpine family, Crassulaceae. The roughly seven species it contains are distributed in Texas in the United States and northeastern Mexico. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek words ληνός (lenos), meaning “trough”, and φύλλον (phyllon), meaning “leaf.”
Examples of Lenophyllum succulents:




Lithops
Lithops (commonly called “flowering stones” or “living stones”) are true mimicry plants: their shape, size and color cause them to resemble small stones in their natural surroundings. The plants blend in among the stones as a means of protection.
Lithops is a genus of succulent plants in the ice plant family, Aizoaceae. Members of the genus are native to southern Africa.
Examples of Lithops succulents:




Related Posts:
Lithops Life Cycle, Characteristics and Care
x Mangave
x Mangave is an intergeneric hybrid derived from crosses of two North American genera, Agave and Manfreda. x Mangave is often employed as an ornamental plant in dry environments, as the hybrid possesses traits of durability found in both Agave and Manfreda.
The plant appears as a compact, symmetrical agave with succulent leaves. It grows up to four feet high and six feet wide. The leaves of the plant are stiff, fragile, and variable in foliage color and patterns. × Mangave flowers in June and July, producing brown flowers.
× Mangave inherits the drought-resisting traits of both parent plants. They can resist high temperatures and direct sunlight, but prefer shade. The plant can survive below-freezing temperatures but can become damaged if the temperature drops below -6 degrees Celsius.
Examples of x Mangave succulents:




Monanthes
Monanthes is a genus of small, succulent, subtropical plants of the family Crassulaceae. The about ten species are mostly endemic to the Canary Islands and the Savage Islands, with some found on Madeira.
Monanthes are not frost-resistant. They are linked with the genera Sempervivum, Greenovia, Aichryson and Aeonium, which is obvious from their similar flowers.
Examples of Monanthes succulents:




Monilaria
The plant genus Monilaria belongs to the Aizoaceae family or the fig-marigold family. The Monilaria are succulents native to South Africa.
Examples of Monilaria succulents:




Neohenricia
Neohenricia is a genus of succulent plants in the family Aizoaceae. Neohenricia is a small (tiny) cousin of similar-looking species like Titanopsis, Aloinopsis, Rhinephyllum all with rough leaves but its tiny flowers on summer nights exhale a powerful tropical fragrance, perhaps the finest odor of all Mesembryanthemum — mixture of pineapple, coconut, and something musky.
The collective scent can be detected many meters apart. What is really interesting is that at the beginning the color of the flowers is whitish or greenish not lilac or purple. But after a day or two, it becomes normal purple color.
Examples of Neohenricia succulents:


Odontophorus
Odontophorus is a genus of succulent plants in the family Aizoaceae.
Examples of Odontophorus succulents:




Orbea
Orbea is a genus of flowering plants of the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1812. It is native to Africa.
Orbeas are leafless, glabrous, succulent perennials that form compact to diffuse clumps. They branch from the base and often arise from rhizomatous rootstocks. The stems are erect to prostrate and sometimes exhibit a creeping nature. The four-angled stems are usually prominently sharp-toothed, with a soft tip. They usually have well-developed, tooth-like projections (tubercles) on the flanks and are always mottled purplish maroon on a green background, especially distinct when exposed to the sun. At the base of the tubercles, a pair of stipular denticles are found and the stems are without any well-developed leaves.
Examples of Orbea succulents:




Orostachys
Orostachys is a genus of the succulent family Crassulaceae (stonecrop family) that contains about 15 species. It is a biennial herb growing in China, Japan, Kazakhstan, Korea, Mongolia, Russia. Eight species occur in China.
Orostachys are the most morphologically distinct member of subfamily Sedoideae, characterized by a semi-rosette habit, and spadix-like terminal, narrowly pyramidal to the cylindrical inflorescence. leaves are linear to ovate, often with dull purple dots. The stem arrangement is alternate, forming a crowded cauline rosette. The roots are fibrous and it has no rhizome. The flowering stem is solitary, arising from the center of the rosette in the second year.
Examples of Orostachys succulents:




Oscularia
Oscularia is a genus of succulent flowering plants in the family Aizoaceae, native to semi-arid and rocky habitats in the Western Cape of South Africa.
The most superficially recognizable feature of the genus is the strange shape of the leaves, which are grey-green and waxy. They are triangular in cross-section (3 angled) and can be sickle, club or mouth shaped. The name “Oscularia” actually means “group of tiny mouths” in Latin, and refers to the appearance of the toothed leaves in some species. The stems are often red, and the leaves can become red too during times of drought.
Abundant, almond-scented, daisy-like white or pink flowers appear throughout the summer.
Examples of Oscularia succulents:




Othonna
Othonna is a genus of African plants in the Asteraceae family. These are evergreen or deciduous geophytes, dwarf succulents or shrubs concentrated in the Western Cape Province of South Africa and also in southern Namibia. A few species occur in summer rainfall parts of southern Africa. Othonna is closely allied to Senecio and the succulent identifier is in the details of the involucre.
Examples of Othonna succulents:




Pachyphytum
Pachyphytum is a small genus of succulents in the Crassulaceae family, native from Mexico, which lands at 600 to 1,500 meters (2,000 to 4,900 ft) high. The name comes from the ancient Greek pachys (=thick) and phyton (=plant) because of the shape of the leaves.
Examples of Pachyphytum succulents:




Related Posts:
14 Types of Pachyphytum [With Pictures]
x Pachyveria
× Pachyveria is a hybrid cross between Pachyphytum and Echeveria. They typically grow to 2–6 inches.
Examples of xPachyveria succulents:




Related Post:
9 Unique Pachyveria Species [With Pictures]
Peperomia
Peperomia (radiator plant) is one of the two large genera of the family Piperaceae, with more than 1000 recorded species. Most of them are compact, small perennial epiphytes growing on rotten wood.
Peperomia are wonderful plants to grow indoors as they have so many features that make them ideal houseplants.
Examples of Peperomia succulents:




Pleiospilos
Pleiospilos is a genus of succulent flowering plants of the family Aizoaceae, native to South Africa. The name is derived from the Greek pleios “many” and spìlos “spot”.
The plants are characterized by their highly succulent, rock-like leaves that are heavily dotted. Pleiospilos nelii, perhaps the most common member of the genus in cultivation, blooms in the winter, while all other species flower in the autumn.
The plants are active in the summer and should be kept dry in the winter, except the popular Pleiospilos nelii, which requires water throughout the winter if it is to do well. They are ideal pot subjects and require a sunny window, but can burn if care is not taken. They are susceptible to red spider mites.
Examples of Pleiospilos succulents:




Related Posts:
9 Types of Pleiospilos [With Pictures]
Portulaca
Portulaca is the type genus of the flowering plant family Portulacaceae, comprising about 40-100 species found in the tropics and warm temperate regions. They are also known as purslanes. Common purslane is widely considered an edible plant, and in some areas it is invasive.
Portulaca is especially well-suited for growing in containers on patios and decks, with its fleshy, succulent leaves, red stems, and colorful cactus-like flowers in shades of red, orange, yellow, pink, purple and white. These succulent plant species prefer hot, dry, almost desert-like conditions.
Examples of Portulaca succulents:




Portulacaria
Portulacaria afra (known as elephant bush, dwarf jade plant, pork bush and spekboom in Afrikaans) is a small-leaved succulent plant found in South Africa. These types of succulent plants commonly have a reddish stem and leaves that are green, but also a variegated cultivar is often seen in cultivation.
Examples of Portulacaria succulents:
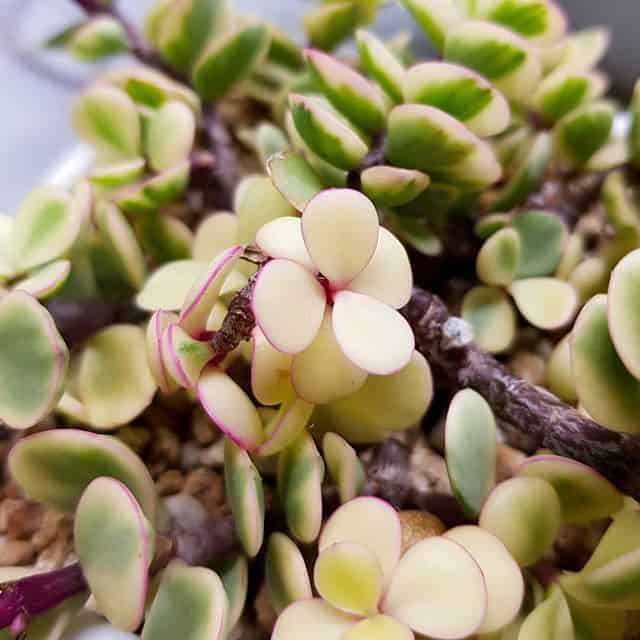




Prenia
Prenia is a genus of succulent plants in the ice plant family Aizoaceae. The species Prenia vanrensburgii is a fast-growing, short-lived perennial succulent, endemic to the sunny, windy, littoral seafront or shoreline zone in the coastal parts of the eastern part of the Western Cape. It is a useful ornamental plant, ideal for seafront gardens.
Examples of Prenia succulents:




Pseudolithos
Pseudolithos is a genus of succulent flowering plants of the family Apocynaceae, indigenous to Somalia, Yemen and Oman.
The plants were first described as a genus in 1965; the name “Pseudo-lithos” means “false-stone” and refers to their pebble-like appearance. All species in this genus are highly succulent, highly reduced, and exhibit tessellation on their stems’ surface. Their small flowers appear on the spherical body’s surface.
Examples of Pseudolithos succulents:




Rabiea
Rabiea is a low-growing mat-forming succulent from South Africa. It is a genus of succulent plants in the family Aizoaceae.
Examples of Rabiea succulents:




Rhombophyllum
Rhombophyllum is a genus of succulent plants which contains approximately 3 to 6 species and belongs to the family of the Aizoaceae. It is native to South Africa, mainly to subtropical thicket vegetation in the Eastern Cape. However, the genus has also been observed in the south-eastern Northern Cape.
Examples of Rhombophyllum succulents:



Rosularia
Rosularia is a small genus of the family Crassulaceae. It includes about 28-35 species from Europe, the Himalayas, and northern Africa.
Rosularia grows in small rosettes with flat green succulent foliage, much like hens and chicks. Depending on the variety, Rosularia foliage often has red, purple or yellow margins that may be covered in tiny hairs, called cilia. When present, these small hairs help plants capture water and nutrients and transport them to the root zone.




Sansevieria
Sansevieria, commonly known as Snake Plant or Mother-in-law’s tongue, is a historically recognized genus of flowering plants in the Dracaenaceae family. Currently included in the genus Dracaena, it is native to Africa, Madagascar and southern Asia.
Examples of Sansevieria succulents:




Related Posts:
32 Types of Snake Plant: Sansevieria Varieties Identification [With Pictures]
x Sedeveria
× Sedeveria is a hybrid cross between Sedum and Echeveria.
Examples of x Sedeveria succulents:




Related Post:
14 Fantastic Sedeveria Hybrid Succulents [With Pictures]
Sedum
Sedum is a large genus of flowering plants in the family Crassulaceae, members of which are commonly known as stonecrops. The genus has been described as containing up to 600 species, subsequently reduced to 400–500. The plants vary from annual and creeping herbs to shrubs.
Sedum is a genus that includes annual, biennial, and perennial herbs. They are characterized by succulent leaves and stems. The extent of morphological diversity and homoplasy make it impossible to characterize Sedum phenotypically.
Examples of Sedum succulents:




Related Posts:
130+ Attractive Sedum Varieties [With Pictures]
Sempervivum
Sempervivum is a genus of about 40 species of flowering plants in the Crassulaceae family, commonly known as houseleeks. Other common names include liveforever (the source of the taxonomical designation Sempervivum, literally “always/forever alive”) and hen and chicks, a name shared with plants of other genera as well. They are succulent perennials forming mats composed of tufted leaves in rosettes. In favorable conditions, they spread rapidly via offsets, and several species are valued in cultivation as groundcover for dry, sunny locations.
Sempervivums exist from Morocco to Iran, through the mountains of Iberia, the Alps, Carpathians, Balkan mountains, Turkey, the Armenian mountains, in the northeastern part of the Sahara Desert, and the Caucasus. Their ability to store water in their thick leaves allows them to live on sunny rocks and stony places in the mountain, subalpine and alpine belts. Most are hardy to US zone 4 and will handle warm climates to about zone 8.
Examples of Sempervivum succulents:




Senecio
Senecio is a genus of succulent plants in the family Asteraceae. The name of the genus means “old man”.
There are about 100 succulent Senecios. There are some large shrub succulent varieties, but many are small, trailing plants or spreading ground covers.
Examples of Senecio succulents:




Related Posts:
24 Senecio Lower Classifications [With Pictures]
Sinocrassula
Sinocrassula is a genus of succulent, subtropical plants of the family Crassulaceae. The name “Sinocrassula” means “Chinese crassula”. They come from the province Yunnan in the south of China, and also from the north of Burma. They grow at an altitude between 2.500 and 2.700 m.
Sinocrassula presents rosettes of thin fleshy triangular brown leaves. The plants are up to 20 cm in height. They develop dense clumps. Sometimes, Sinocrassula shows monstrous forms. The inflorescence is a dense panicle up to 10–15 cm with whitish flowers and red-tipped petals.



Stapelia
Stapelia is a genus of low-growing, spineless, stem succulent plants, predominantly from South Africa with a few from other parts of Africa. Known globally as African starfish flowers, and locally as carrion flowers, members of the genus Stapelia are usually characterized by their foul-smelling flowers reminiscent of the odor of rotting meat.
The Stapelia hairs, coloration and surface mimic decaying animal matter and attract mostly flies, which act as pollinators. The strong carrion scent is sometimes recognizable at a great distance, especially on hot afternoons. Like other members of the Stapeliads, these types of succulent plants look like cactus and are often mistaken as such.
Examples of Stapelia succulents:




Related Post:
34 Types of Stapelia [With Pictures]
Stapelianthus
Stapelianthus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1933. The entire genus is endemic to Madagascar and is concentrated in the far south of the island. The genus is defined by the unique corona structure of its flowers.
Examples of Stapelianthus succulents:




Stapeliopsis
Stapeliopsis is a genus of succulent plants in the family Apocynaceae, native to southern Africa.
Examples of Stapeliopsis succulents:




Tavaresia
Tavaresia is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1902. It is native to southern Africa.
Examples of Tavaresia succulents:




Titanopsis
Titanopsis is a genus of about 10 species of succulent plants of the family Aizoaceae, indigenous to the arid regions of South Africa and Namibia. The name “Titanopsis” comes from the ancient Greek “titanos” (limestone) and “opsis” (looking like).
Naturally growing in the Upper Karoo in South Africa, it is an attractive but quite unusual plant because of its formation.
Examples of Titanopsis succulents:




Trachyandra
Trachyandra is a genus of plant in the family Asphodelaceae, subfamily Asphodeloideae, first described as a genus in 1843. It is native to eastern and southern Africa, as well as to Yemen and Madagascar. Many of the species are endemic to South Africa.
Examples of Trachyandra is a genus of plant in the family Asphodelaceae, subfamily Asphodeloideae, first described as a genus in 1843. It is native to eastern and southern Africa, as well as to Yemen and Madagascar. Many of the species are endemic to South Africa.
Examples of Trachyandra succulents:



Tradescantia
Tradescantia (commonly known as Wandering Jew, Spiderwort or Indian paint) is a genus of 75 species of herbaceous perennial wildflowers in the family Commelinaceae, native to the New World from southern Canada to northern Argentina, including the West Indies.
Examples of Tradescantia succulents:




Trichodiadema
Trichodiadema is a genus of succulent plants of the family Aizoaceae. Trichodiademas are small, short-stemmed succulents with small, elongated, alternating sections measuring 8 mm long. They are grey and green. At the apex of each alternating section is a ring of small bristles radiating around the center, that gives the appearance of a cactus areola.
Trichodiadema looks surprisingly like a cactus but is not a cactus. Its leaves are succulent and end in a circle of stiff hairs, giving the plant a similar appearance to some species in the cactus genus Mammillaria.
Examples of Trichodiadema succulents:




Tromotriche
Tromotriche is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae. It is native to southern Africa. Its Greek name refers to the quivering hairs that surround the lobes of its flowers (“tromo”, meaning “trembling” and “trichos”, meaning “hair”).
Examples of Tromotriche succulents:




Tylecodon
Tylecodon is a genus of succulent plants in the family Crassulaceae, native to southern Africa. Until the late 1970s all these succulent plant species were included in the genus Cotyledon, but in 1978 Helmut Toelken of the Botanical Research Institute, Pretoria split them off into a genus of their own.
Tylecodon species are poisonous. Some of them are sufficiently hazardous to livestock to constitute an economic problem for stock farmers. Concerns also have been expressed on potential risks to collectors who handle the plants carelessly. The various species and even individual plants do however vary greatly in toxicity.
Examples of Tylecodon succulents:




Umbilicus
Umbilicus is a genus of over ninety species of flowering plants in the family Crassulaceae.
Examples of Umbilicus succulents:




Xerosicyos
Xerosicyos is a flowering plant genus of the family Cucurbitaceae. Its name comes from Greek xeros (meaning “dry”) and sicyos (“cucumber”). There are three species, all endemic to Madagascar.
Xerosicyos danguyi is a large liana with thick stems and round, gray succulent leaves. It is commonly called the “Silver Dollar Plant”, “String of Coins Plant”, “Dollar Vine” or “Penny Plant”.
Examples of Xerosicyos succulents:



Yucca
Yucca is a genus of about 40 species of succulent plants in the agave subfamily of the asparagus family (Asparagaceae), native to southern North America. Most species of yucca are stemless, with a rosette of stiff sword-shaped leaves at the base and clusters of waxy white flowers.
Examples of Yucca succulents:
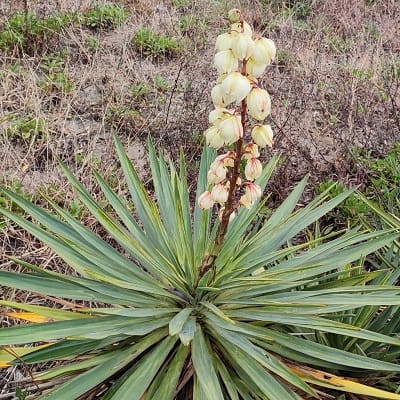
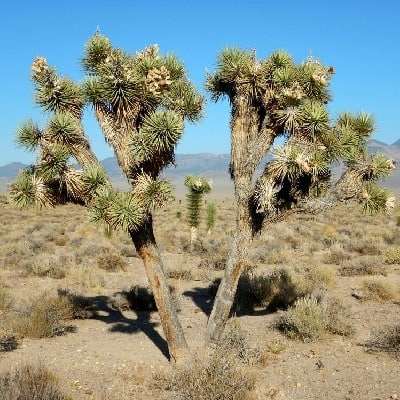
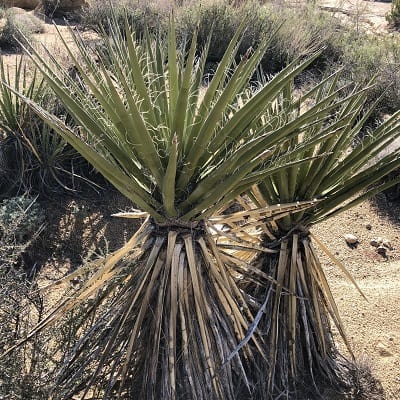



Related Post:
61 Types Of Yucca Plants [With Pictures]
How do I Identify a Succulent?
Succulents have water-filled leaves. In fact, a “succulent” is just another name for a “xerophyte.” A “xerophyte” is simply a plant that grows in dry soil. That doesn’t mean it can’t also grow in water – it just means it requires very little moisture. If you’re looking to identify a succulent plant, using a succulent identifier app can be helpful.

Sources:
https://en.wikipedia.org/
https://www.theplantlist.org/
https://pza.sanbi.org/
https://www.succulentguide.com/
https://www.llifle.com/
https://www.giromagicactusandsucculents.com/
https://www.lithops.info/

this is an awesome site, thank you. finally able to identify a couple of my plants i have been wondering about.
Hi Meggs, glad that you’ve benefited from this post!
wonderful to widen our knowledge. The botantical names are hard for a common person to remember but the photos are wonderful. Thank you for sharing your collation with us.
What gorgeous pictures and a wealth of knowledge! Thanks so much for posting!
Excellent site ! Nice pictures, very helpful and informative explanations for caring for my new hobby of growing succulents! Will come back to learn more !